Self-Consistent Ice Mass Balance and Regional Sea Level from Time-Variable Gravity
by T. C. Sutterley, I. Velicogna and C.-W. Hsu
Earth and Space Science (2020)
Abstract:
Measurements of time-variable gravity from the Gravity Recovery and
Climate Experiment (GRACE) and the GRACE Follow-on (GRACE-FO)
missions are an invaluable tool for monitoring changes in mass of
the Earth's glaciated regions. We improve upon estimates of glacier
and ice sheet mass balance from time-variable gravity by including
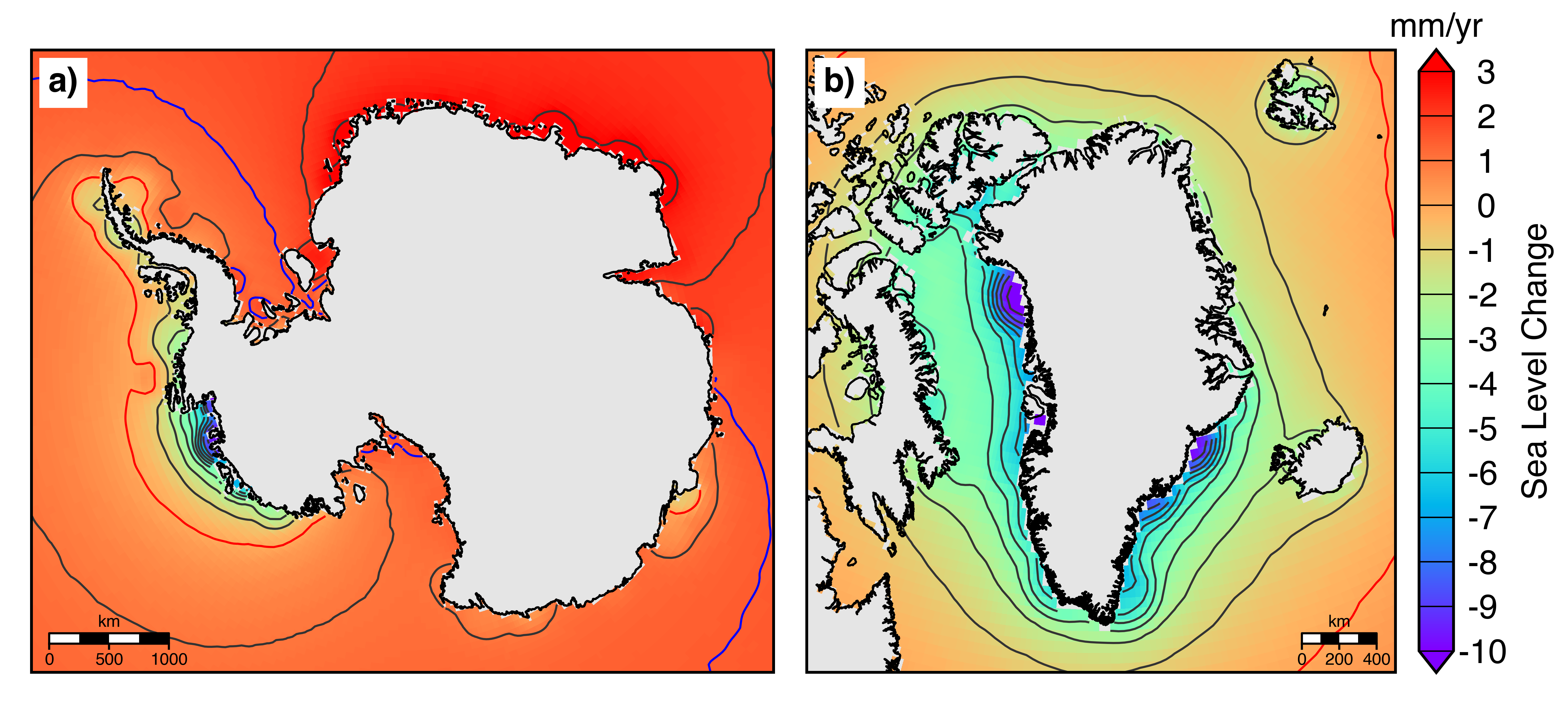
instantaneous spatiotemporal variations in sea level. Here, a
least-squares mascon technique is combined with solutions to the
sea level equation to iteratively correct the GRACE/GRACE-FO data
for the induced sea level response on a monthly basis. We find that
variations in regional sea level affect ice sheet mass balance
estimates in Greenland by approximately 4% and in Antarctic by
approximately 5%. Since 2002, the Greenland ice sheet has been
losing mass at an average rate of 263±23 Gt/yr, and the
Antarctic ice sheet has been losing mass at average rates between
-90±52 Gt/yr and -122±53 Gt/yr depending on the rate of
Glacial Isostatic Adjustment (GIA). The mass losses from both ice
sheets represent an increase of 15.6±2.0 mm to global mean sea
levels since 2002.
Data Access
This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.