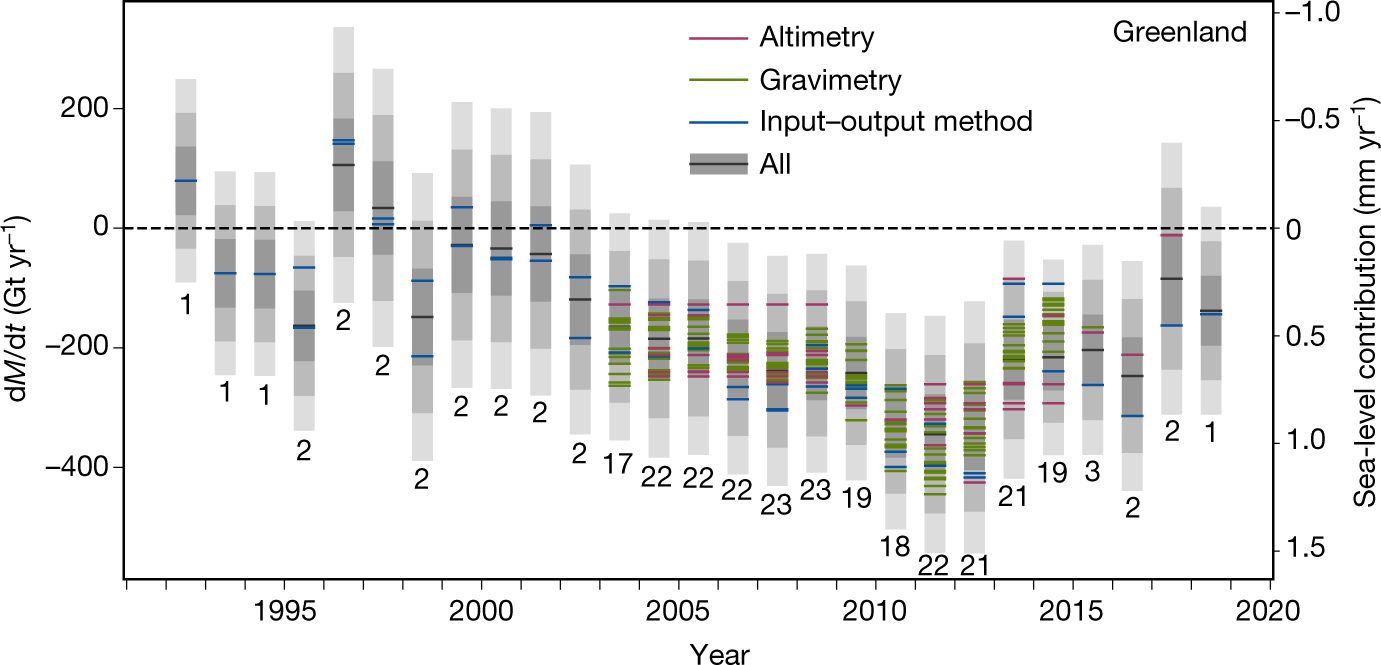
Mass balance of the Greenland Ice Sheet from 1992 to 2018
by A. Shepherd, E. Ivins, E. Rignot, B. Smith, M. van den Broeke, I. Velicogna, P. Whitehouse, K. Briggs, I. Joughin, G. Krinner, S. Nowicki, T. Payne, T. Scambos, N. Schlegel, G. A, C. Agosta, A. Ahlstrøm, G. Babonis, V. R. Barletta, A. A. Bjørk, A. Blazquez, J. Bonin, W. Colgan, B. Csatho, R. Cullather, M. E. Engdahl, D. Felikson, X. Fettweis, R. Forsberg, A. E. Hogg, H. Gallee, A. Gardner, L. Gilbert, N. Gourmelen, A. Groh, B. Gunter, E. Hanna, C. Harig, V. Helm, A. Horvath, M. Horwath, S. Khan, K. K. Kjeldsen, H. Konrad, P. L. Langen, B. Lecavalier, B. Loomis, S. Luthcke, M. McMillan, D. Melini, S. Mernild, Y. Mohajerani, P. Moore, R. Mottram, J. Mouginot, G. Moyano, A. Muir, T. Nagler, G. Nield, J. Nilsson, B. Noël, I. Otosaka, M. E. Pattle, W. R. Peltier, N. Pie, R. Rietbroek, H. Rott, L. Sandberg Sørensen, I. Sasgen, H. Save, B. Scheuchl, E. Schrama, L. Schröder, K.-W. Seo, S. B. Simonsen, T. Slater, G. Spada, T. Sutterley, M. Talpe, L. Tarasov, W. J. van de Berg, W. van der Wal, M. van Wessem, B. D. Vishwakarma, D. Wiese, D. Wilton, T. Wagner, B. Wouters, J. Wuite, and The IMBIE Team. Nature (2019)
Abstract:
The Greenland Ice Sheet has been a major contributor to global
sea-level rise in recent decades, and it is expected to continue to
be so. Although increases in glacier flow and surface melting have
been driven by oceanic and atmospheric warming, the magnitude and
trajectory of the ice sheet's mass imbalance remain uncertain. Here
we compare and combine 26 individual satellite measurements of
changes in the ice sheet's volume, flow and gravitational potential
to produce a reconciled estimate of its mass balance. The ice sheet
was close to a state of balance in the 1990s, but annual losses have
risen since then, peaking at 345 ± 66 billion tonnes per year
in 2011. In all, Greenland lost 3,902 ± 342 billion tonnes of
ice between 1992 and 2018, causing the mean sea level to rise by
10.8 ± 0.9 millimetres. Using three regional climate models,
we show that the reduced surface mass balance has driven
1,964 ± 565 billion tonnes (50.3%) of the ice loss owing
to increased meltwater runoff. The remaining 1,938 ± 541
billion tonnes (49.7%) of ice loss was due to increased
glacier dynamical imbalance, which rose from 46 ± 37 billion
tonnes per year in the 1990s to 87 ± 25 billion tonnes per
year since then. The total rate of ice loss slowed to 222 ± 30
billion tonnes per year between 2013 and 2017, on average, as
atmospheric circulation favoured cooler conditions and ocean
temperatures fell at the terminus of Jakobshavn Isbræ.
Cumulative ice losses from Greenland as a whole have been close to
the rates predicted by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
for their high-end climate warming scenario, which forecast an
additional 70 to 130 millimetres of global sea-level rise by 2100
compared with their central estimate.